by : Dr. Mohammad Reza Chitsaz
Russia's invasion of Ukraine could have a profound effect on the lives of people around the world. It is one of the most strategic regions of the world which is deeply affected by this crisis is the Middle East. This impact can be evaluated in different dimensions. In fact, the effects of this international challenge are so far-reaching and profound that it could affect the Middle East in terms of security, policy, and economy. Accordingly, in the following article, we will try to examine and analyze the impact that this crisis has on the Middle East region in various aspects.
Military-Security Dimensions of War
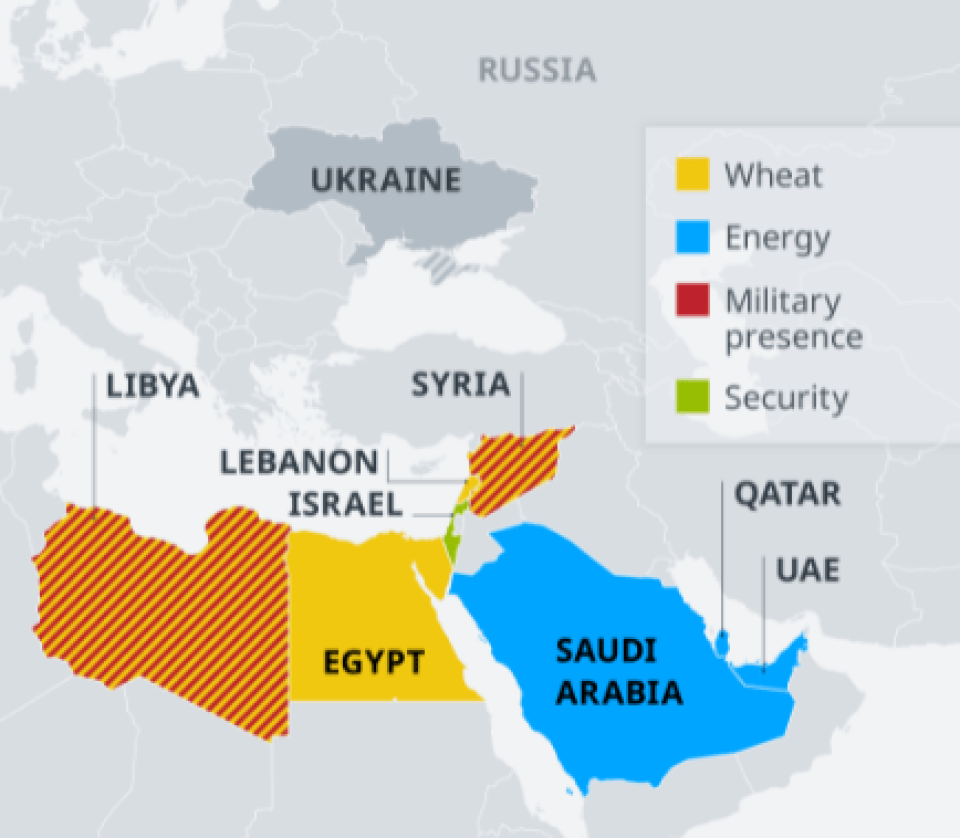
One aspect of the Russia-Ukraine war in the Middle East is the military and security dimensions of the crisis. Russia is an important player in this field because it has a military and logistics presence in many countries in the region, such as Syria and Libya. For example, one of the consequences of this war could be the escalation of instability in Libya, as the balance of power in Libya will be upset. Literally, in the near future we will probably see an increase in tensions and conflicts in Libya between the two sides involved in this country. Moscow, one of the main backers of one side in the Libyan conflict, Caliph Haftar, is likely to have a smaller presence in the country due to the war with Ukraine, which could escalate clashes between UN-backed forces in Tripoli and Khalifa Haftar's supporters in eastern Libya. However, Moscow can put pressure on Europe by creating a new wave of asylum seekers coming to Europe from Libya. In addition, Russia could mobilize its military forces to attack Ukraine in the short term through the Al-Jafra air base in eastern Libya [1].
Another issue that is likely to be affected by developments in Eastern Europe is the Iran-Israel war in Syria. Russia is the biggest international player in the Syrian crisis, and while the country has so far remained silent and unresponsive to Israeli attacks on Iranian-backed forces in Syria, the Russia-Ukraine war is likely to disrupt all these predictions. Since Tel Aviv has been forced to choose between the United States and the Western world in the midst of this crisis, it may have to pay for it in Syria, and from now on it will face a backlash from Moscow, with Putin effectively considering it responsible for attacking Iran-backed forces. In addition, Israel may face an immigration crisis as a result of the Moscow-Kyiv war. In fact, there are many Jews living in Ukraine who, as a result of the war, may migrate to Israel [2].
Eventually, this crisis could involve Turkey in the war as well, as the country is somehow involved in the war. The Black Sea is connected to the open sea by two straits through the Mediterranean Sea; the Bosphorus Strait, which connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles, which connects the Sea of Marmara to the Aegean Sea. According to the Treaty of Montreux, signed in 1936, Turkey controls the two straits. That is exactly why Ukrainian President Vladimir Zelinsky has called on Turkey to close the Strait of the Black Sea to the Russian navy and prevent Russian troops from crossing [3].
Energy Section

Perhaps it can be said that one of the most important dimensions of this crisis is the impact of the energy sector. While Russia supplies 40 percent of Europe's gas and 25 percent of the continent's oil, the Moscow-Kyiv conflict is likely to lead to a paradigm shift in the energy market. On one hand, we see that with the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the price of oil and gas is increasing. This trend could be to the benefit of the region, as many countries in the Middle East and the Persian Gulf export these underground resources. This is especially true in the case of Iran, provided that Iran's nuclear negotiations with world powers are concluded as soon as possible and that Iran can return to the world market. It is estimated that Iran currently has more than 100 million barrels of oil reserves, which could help stabilize it at a time when the global market is facing a shortage of 400,000 barrels per day and reduce the government's budget deficit in Tehran [4].
This crisis will add to the importance of countries such as Qatar and Saudi Arabia, as these two countries are the largest exporters of gas and oil in the world, respectively, and it is expected that in the long run, especially European countries will rely more on these two oil and gas giants. The issue was discussed between the Emir of Qatar during a recent visit to the United States in late January and during a meeting with US President Joe Biden. In this critical situation, Qatar's supply of European gas will both help the world's public perception of the country and make it a strategic partner for Europe in the long run. Interestingly, this trend coincides with the country's plan to further develop liquefied natural gas (LNG) production, which will be pursued by the country in the future. In such a situation, Egypt is another option. It could also rush to Europe's aid and reduce the energy crisis in Europe to some extent by producing liquefied natural gas [5].
At the same time, Saudi Arabia, as the largest oil producer, can reduce the negative consequences of the oil shortage to some extent by increasing its production in the oil sector. This approach of the Saudi government can reduce the negative mentality created in the West against Muhammad bin Salman: the mentality that was created by the assassination of Jamal khashoggi by the Saudi government and the role of bin Salman in it and had its impact in various dimensions. This solution will be successful, especially if it is accompanied by increased oil production in Iraq and Kuwait. It is estimated that the three countries could increase their production to a total of 4 million barrels per day, and to some extent replace Russia in the oil market if it faces extensive banking and financial sanctions [6].
But on the other hand, what adds to the complexity of the issue is the relations that Moscow and Riyadh have with each other. In August last year, a military agreement was signed between Saudi Arabia and Russia. The recent crisis will put Saudi Arabia at a crossroads between Moscow and Washington, and it will have to choose the one that will most likely be the US option. Adding to the complexity is the cooperation between Moscow and Riyadh over the past few years on oil prices. The price of oil, which has been fluctuating and falling sharply over the past few years, has reached relative stability with the collective cooperation of the major producing countries. At the head of this cooperation were two oil giants, Saudi Arabia and Russia, one of which led OPEC and the other led by the so-called OPEC Plus. The recent crisis will affect the oil cooperation of the two countries and will most likely separate the two countries [7].
Food and agricultural crisis

The conflict in Ukraine will also pose a challenge to food security in the Middle East. Ukraine, known for centuries as the European Breadbasket, is the supplier of grain to many countries in the Middle East, especially wheat. Lebanon, for example, imports about 700,000 tons of wheat annually from Ukraine, which accounts for about 50 percent of the country's wheat consumption. More importantly, Russia itself is the world's largest producer of wheat, and together with Ukraine they produce a quarter of the world's wheat. Moreover, recent crisis could severely affect Egypt, the world's largest importer of wheat. It is estimated that about 80% of wheat exports to Egypt are made by Russia and Ukraine. In this regard, Egyptian government spokesman Nasser al-Saad warned that the recent conflict could affect Egypt's wheat reserves, and the Egyptian people must save on bread so that bread is not rationed. [8]
Literally, the Middle East region, and especially the Arab world, which has not yet been able to recover from the recent drought, is now likely to face a crisis of rising prices due to this war. This is particularly important because bread is the dominant food in the Middle East, and it can contribute to the political instability that pervades the region. It can be clearly seen from the uprisings in the region in 2011 when the experts cite one of the causes and factors of the unrests as rising food prices.
Overall, the outbreak of war and crisis in Eastern Europe will have a profound effect on the Middle East. According to John Mersheimer, the conflict is the product of Western mistakes and Western intervention in Ukraine and NATO's development to Eastern Europe. On the one hand, in the field of food and agricultural products, it can lead to food shortages and insecurity in the region [9]. The West, and especially Europe, is likely to become more dependent on the Middle East in terms of Oil and gas. This will happen especially in the long run, and the countries of the region can use it as a lever of pressure against the West. In addition, the Middle East will become increasingly important to the United States and Europe, and US macro-strategy will be challenged significantly. In fact, given the current situation, the hypothesis that the United States will easily leave the Middle East and turn its full attention to China will fade a bit.
Source:
- Andreas Illmar, How Ukranian Crisis affect the Middle East, February 15, 2022, https://www.dw.com/en/how-could-the-ukraine-crisis-affect-the-middle-east/a-60802745
- Ibid
- Al-Monitor Staff, How Russia’s assault on Ukraine affects MidEast, February 27 2022, https://www.al-monitor.com/originals/2022/02/live-updates-how-russias-assault-ukraine-affects-mideast,
- Jonathan Tirone and Golnar Motevalli, Russian Invasion Puts Endgame of Iran Nuclear Talks in Jeopardy, February 24, 2022, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-02-24/russian-invasion-puts-endgame-of-iran-nuclear-talks-in-jeopardy
- Cristian-Dan Tatarua, The potential impact of Ukraine-Russia conflict on the MENA region, February 7, 2022, https://www.mei.edu/publications/potential-impact-ukraine-russia-conflict-mena-region
- Ibid
- Asli Aydinatsabas, Julien Barnes-Dacey, Cinzia Biansco, Hugh Lovatt, Tarek Megerisi, Kelly Petillo, Unsettled: The impact of the Russia-Ukraine crisis on the Middle East and North Africa, February 10, 2022, European Council on Foreign Relations, https://ecfr.eu/article/unsettled-the-impact-of-the-russia-ukraine-crisis-on-the-middle-east-and-north-africa/
- Ukraine Crisis Sparks Frenzy in Global Agriculture Trade, February 25, 2022, https://www.agribusinessglobal.com/markets/ukraine-crisis-sparks-frenzy-in-global-agriculture-trade/
9- John Mearsheimer, Why the Ukrainian Crisis is the West’s Fault, Foreign Affairs, https://www.mearsheimer.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Why-the-Ukraine-Crisis-Is, September/October, 2014, p.1